理清文章框架、概括段落大意是雅思阅读考试中重点考查的技能,而快速抓住段落的主题句,则能起到事半功倍的效果。
雅思考试的阅读部分中,涉及概括能力的题型主要有heading题、summary题和部分的段落配对题。主题句一般出现在什么位置?具有什么特征?如何快速地判断主题句?看这一篇就够了。
雅思阅读题主题句的特征
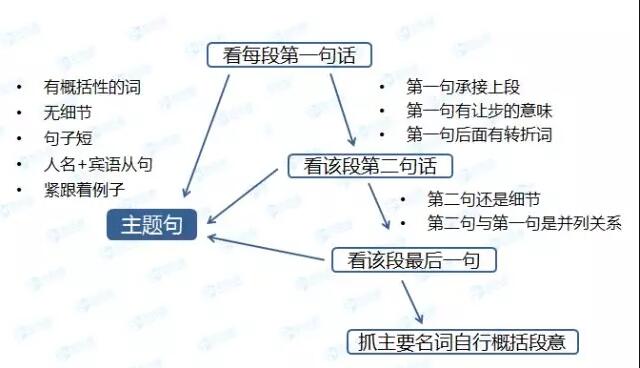
主题句的位置: 根据对剑4到剑12文章的分析,段落句是主题句的情况多达65%,约10%的段落是第二句为主题句,另有约5%的段落最后一句为主题句。当然也有找不出明显主题句的段落,这部分约占20%。所以阅读文章时,我们需要从每段的句开始,按照以下原则来确定主题句,从而概括出段落大意。
段落句是主题句,通常具有以下特征:
1 首句有概括性的词,如:
The sense of vision is developed to different degrees in different species. Baleen species studied at close quarters underwater — specifically a grey whale calf in captivity for a year, and free-ranging right whales and humpback whales studied and filmed off Argentina and Hawaii — have obviously tracked objects with vision underwater, and they can apparently see moderately well both in water and in air. However, the position of the eyes so restricts the field of vision in baleen whales that they probably do not have stereoscopic vision.
—剑4 Test 1 Passage 2 Paragraph 3
上述例子中,different degrees就是有概括性的词,整段都围绕着“不同鲸鱼的视觉差异”展开。
由于主题句要统领整个段落,一般无过多的细节,故而句子较短。类似的情况还可以在剑4 Test 2 Passage 1 Paragraph 1和 剑5 Test1 Passage 3 Paragraph 2 见到。
2 首句为“人名+宾语从句”的格式,大概率上也可判定为主题句,如:
Earlier this year, Sergio Pellis of Lethbridge University, Canada, reported that there is a strong positive link between brain size and playfulness among mammals in general. Comparing measurements for fifteen orders of mammals, he and his team found larger brains (for a given body size) are linked to greater playfulness. The converse was also found to be true. Robert Barton of Durham University believes that, because large brains are more sensitive to developmental stimuli than smaller brains, they require more play to help mould them for adulthood.‘I concluded it's to do with learning, and with the importance of environmental data to the brain during development.' he says.
—剑4 Test 2 Passage 3 Paragraph E
剑6 Test 2 Passage 1 Paragraph A,也是类似的情况。若句不太明显,不足以断定是否为主题句,可快速地看一下第二句。首句后紧跟着例子或解释,也可坐实首句是主题句。如:
But volcanoes are not very predictable. That is because geological time is not like human time. During quiet periods, volcanoes cap themselves with their own lava by forming a powerful cone from the molten rocks slopping over the rim of the crater; later the lava cools slowly into a huge, hard, stable plug which blocks any further eruption until the pressure below becomes irresistible. In the case of Mount Pinatubo, this took 600 years.
—剑4 Test 3 Passage 2 Paragraph D1
上述例子中,第二句是对句的解释。还有一种类似的情况,第二句由for example开头的,像剑4 Test 1 Passage 1 Paragraph 1和剑4 Test 4 Passage 1 Paragraph 8,也能坐实句是主题句。
3 首句提出了问题,如:
Why do people reject the language of their parents? It begins with a crisis of confidence, when a small community finds itself alongside a larger, wealthier society, says Nicholas Ostler, of Britain's Foundation for Endangered Languages, in Bath. 'People lose faith in their culture,' he says. 'When the next generation reaches their teens, they might not want to be induced into the old traditions.’
—剑4 Test 2 Passage 1 Paragraph 4
哪些情况不是主题句
如果段落句具有以下特征,则不是主题句:句只是承接上一段,没有讲新的观点/事物,如:
Here we have two radically different explanations for why so many teacher-subjects were willing to forgo their sense of personal responsibility for the sake of an institutional authority figure. The problem for biologists, psychologists and anthropologists is to sort out which of these two polar explanations is more plausible. This, in essence, is the problem of modern sociobiology-to discover the degree to which hard-wired genetic programming dictates, or at least strongly biases, the interaction of animals and humans with their environment, that is their behaviour.
—剑5 Test 1 Passage 2 Paragraph I
此时就应该意识到这个首句仅仅起到承上启下的作用,没有概括段落的功能。虽然句没有承接上段,但是有让步的意味,也不适合做主题句。如
Identifying genetically talented individuals is only the first step. Michael Yessis, an emeritus professor of Sport Science at California State University at Fullerton, maintains that ‘genetics only determines about one third of what an athlete can do. But with the right training we can go much further with that one third than we've been going.’Yessis believes that U.S runners, despite their impressive achievements, are ‘running on their genetics'. By applying more specific methods, 'they're going to go much faster'. These methods include strength training that duplicates what they are doing in their running events as well as plyometrics, a technique pioneered in the former Soviet Union.
—剑4 Test 4 Passage 1 Paragraph 3
该句的“only the first step”就含有让步的意味。另外,如果在紧接着的第二句话中,看到有however,but,instead等转折词或出现否定前一句话的词,也说明句话不是主题句。详见下面的例子:
There is a widespread belief that increasing wealth encourages people to live farther out where cars are the only viable transport. The example of European cities refutes that. They are often wealthier than their American counterparts but have not generated the same level of car use. In Stockholm, car use has actually fallen in recent years as the city has become larger and wealthier. A new study makes this point even more starkly. Developing cities in Asia, such as Jakarta and Bangkok, make more use of the car than wealthy Asian cities such as Tokyo and Singapore. In cities that developed later, the World Bank and Asia Development Bank discouraged the building of public transport and people have been force to rely on cars — creating the massive traffic jams that characterize those cities.
—剑6 Test 2 Passage 1 Paragraph C
若第二句具备“提及新观点/事物且有概括性的词”或“句中有转折词”的特征,基本上可判定为主题句,如:
Stories about the problems of tourism have become legion in the last few years. Yet it does not have to be a problem. Although tourism inevitably affects the region in which it takes place, the costs to these fragile environments and their local cultures can be minimized. Indeed, it can even be a vehicle for reinvigorating local cultures, as has happened with the Sherpas of Nepal's Khumbu Valley and in some Alpine villages. And a growing number of adventure tourism operators are trying to ensure that their activities benefit the local population and environment over the long term.
—剑5 Test 4 Passage 1 Paragraph C1
但是,如果第二句依然在讲细节,或者第二句话与句构成并列的关系,说明第二句也不是主题句。此时,我们不要去看第三句,应该直接跳至段尾,看段落的最后一句话。
段落的最后一句,如果具备以下特征,则可以判定为主题句:1)该句有概括性的词语;2)尾句与本段前面的其他句子形成“例子 — 总结”的关系,如:
All our subjects deemed the circle soft and the square hard. A full 94% ascribed happy to the circle, instead of sad. But other pairs revealed less agreement: 79% matched fast to slow and weak to strong, respectively. And only 51% linked deep to circle and shallow to square. When we tested four totally blind volunteers using the same list, we found that their choices closely resembled those made by the sighted subjects. One man, who had been blind since birth, scored extremely well. He made only one match differing from the consensus, assigning 'far' to square and 'near' to circle. In fact, only a small majority of sighted subject — 53% — had paired far and near to the opposite partners. Thus, we conclude that the blind interpret abstract shapes as sighted people do.
—剑4 Test 1 Passage 3 Paragraph 8
当然,也有可能该段落本身就没有主题句。如果大家读完了句、第二句和最后一句,都没法找到主题句的话,就要自己动手概括段落大意了。大体说来,具备 “介绍背景”、“叙事性强”、“时间/年份多”等特征的段落会比较难找到主题句。
最后,用一个流程图来总结快速判定主题句的方法,拿走不谢哦:
0元领取剑桥雅思系列真题解析、托福TPO、SAT考试真题,更多独家资料免费领取。
